Decoding the 6×2 Truck: A Beginner’s Guide
1. What is a 6×2 Truck? Advantages, Disadvantages, and Applications
1.1. “6×2”: A Simple Explanation of the Axle Configuration
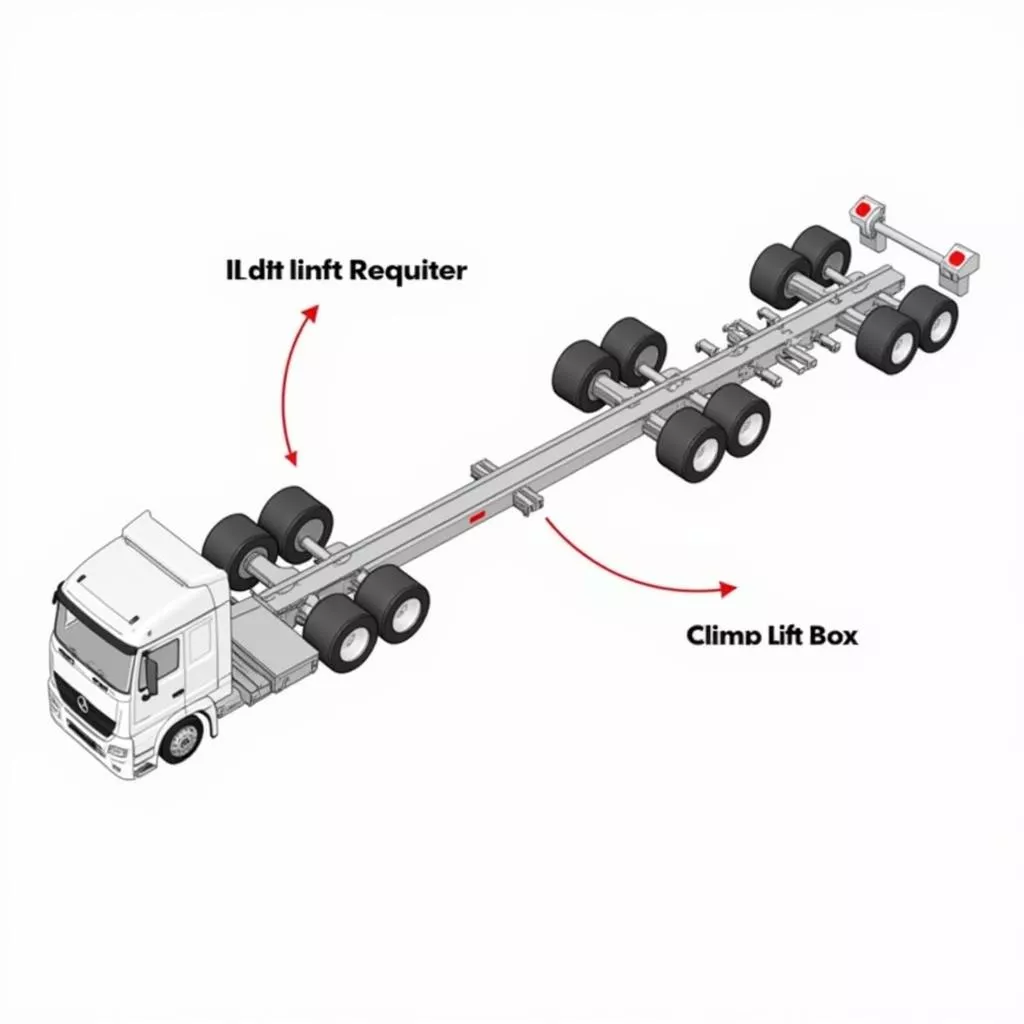
In the trucking world, each wheel that touches the road is considered an “axle”. “6×2” is a formula that represents the wheel configuration, where:
- 6: The total number of wheels.
- 2: The number of driving wheels, i.e., wheels powered by the engine.
- x: Symbol for the axle.
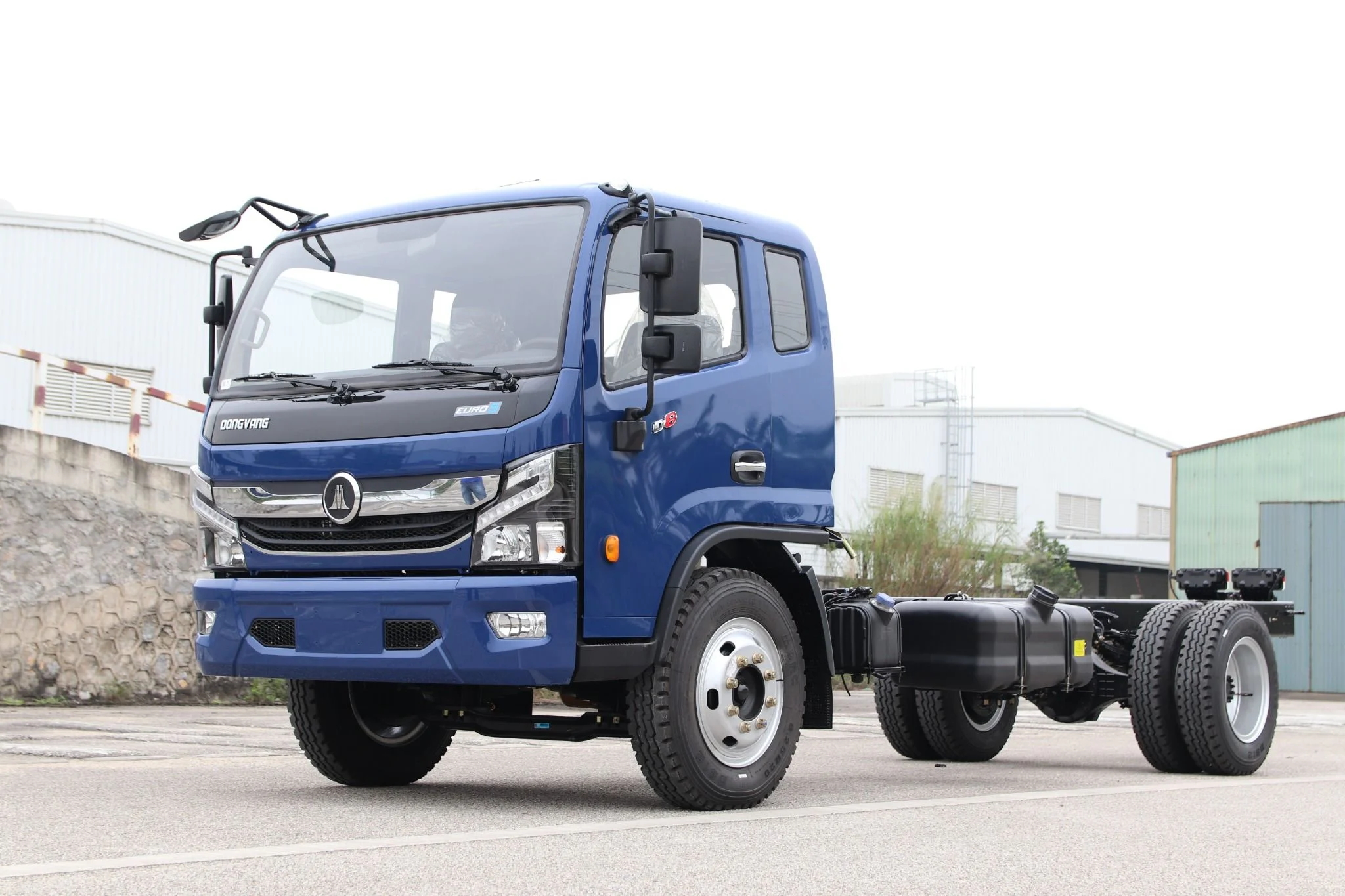
Thus, a 6×2 truck has 3 axles with 2 driving wheels usually located on the rearmost axle. The middle axle with 2 non-driving wheels is called the “lazy” axle, which can be lifted or lowered depending on the load.
 6×2 truck axle configuration
6×2 truck axle configuration
1.2. Advantages of 6×2 Trucks
- Fuel efficiency: When unloaded or lightly loaded, the “lazy” axle can be lifted to reduce friction, thereby reducing fuel consumption.
- Increased tire lifespan: Lifting the “lazy” axle reduces tire wear, extending their lifespan and saving replacement costs.
- High load capacity: When the “lazy” axle is lowered, the truck can carry heavier loads compared to a 4×2 truck with the same permissible load.
 6×2 truck with lifted lazy axle
6×2 truck with lifted lazy axle
1.3. Disadvantages to Consider
- Higher cost: Compared to a 4×2 truck in the same segment, a 6×2 truck has a higher selling price due to its complex structure.
- Limited off-road capability: The additional “lazy” axle makes the 6×2 truck less maneuverable in tight spaces or on rough terrain.
1.4. Common Applications of 6×2 Trucks
6×2 trucks are commonly used in long-haul freight transport, requiring the ability to carry heavy loads such as:
- Transportation of industrial goods and agricultural products.
- Transportation of construction materials.
- Transportation of consumer goods such as beer, soft drinks, etc.
About us

Đào Hoàng LONG
Blog Editor
Chúng Tôi luôn muốn trao đến tay khách hàng một sản phẩm tâm đắc nhất, một chiếc XE TẢI tốt nhất mà mọi người luôn muốn sở hữu.
Recent Posts
XE TẢI HÀ NỘI với kinh nghiệm 10 năm trong nghề xe tải, chúng tôi chuyên cung cấp các dòng xe tải Thùng, xe tải nhẹ, xe tải VAN và các loại xe tải 1 tấn, 2 tấn, 3.5 tấn và xe tải 8 tấn.








