Car Radiator Structure: Importance and Maintenance
“Overheating on long drives is common,” a common saying among long-haul truckers, highlighting the cooling system’s importance, especially for trucks – the livelihood for many families. The radiator is the heart of this system. So, how is a car radiator structured? Let’s delve into the details with Hanoi Trucks!
Car Radiator Structure
1. Overview
The car radiator, also known as the heat exchanger, is a crucial component of the engine cooling system. It absorbs heat from the coolant that has circulated through the engine and dissipates it into the environment, ensuring stable engine operation.
2. Detailed Structure
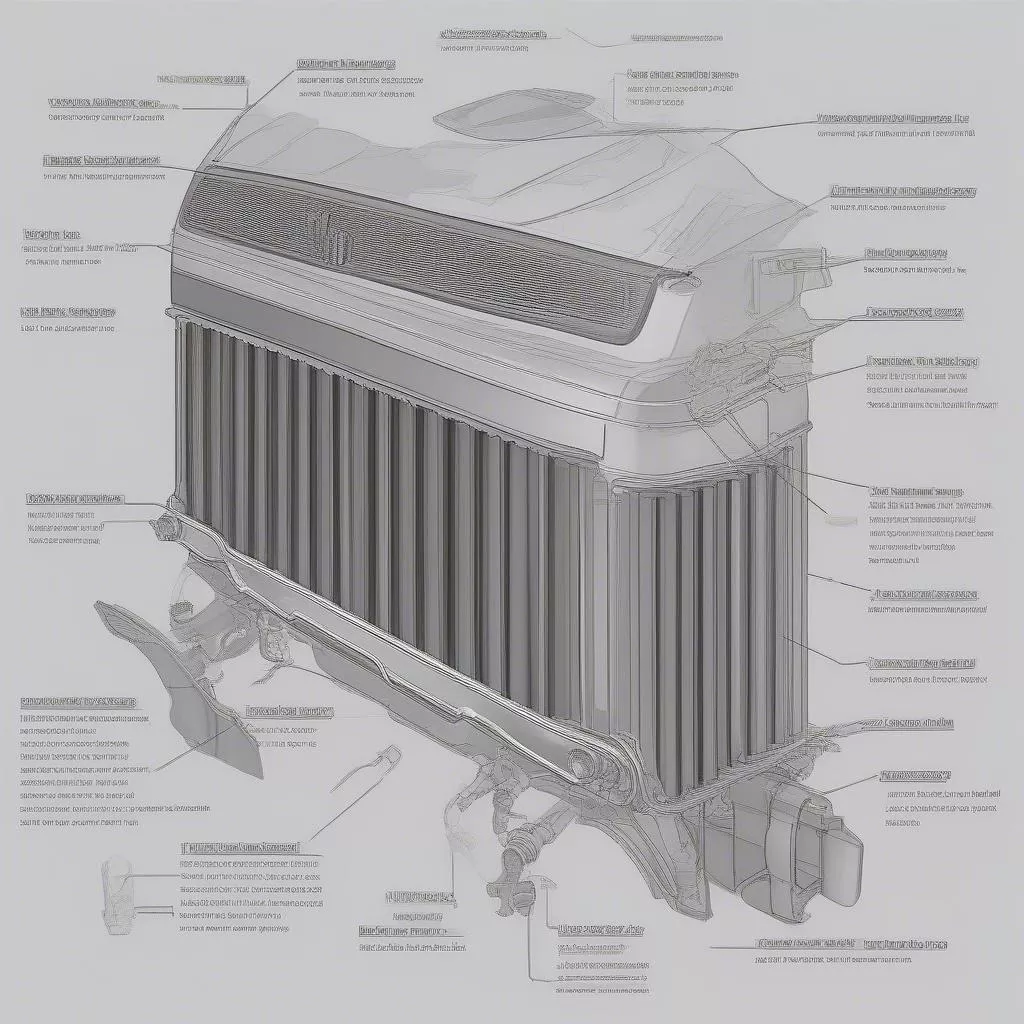
A car radiator typically consists of the following main components:
- Core: Usually made of aluminum or brass with a flat tube or round tube design arranged in parallel, creating narrow gaps for coolant to flow through.
- Fins: Attached between the water tubes, increasing the surface area exposed to air, facilitating faster and more efficient heat dissipation.
- Overflow Tank: Holds a reserve of coolant for the system.
- Radiator Cap: Equipped with a pressure valve, maintaining stable pressure within the cooling system.
- Inlet Hose: Carries hot coolant from the engine into the radiator.
- Outlet Hose: Carries cooled coolant from the radiator back to the engine.
3. Working Principle
When the engine runs, the coolant absorbs heat and is pumped to the radiator. The hot coolant flows through the tubes in the core and transfers heat to the fins. The fan blows air across the fins, carrying the heat away into the atmosphere. The cooled coolant then returns to the engine, continuing the cooling cycle.
To better understand the structure of a car radiator, refer to the illustration below:
 Car radiator structure diagram
Car radiator structure diagram
Car Radiator Price List
| Vehicle Type | Estimated Price (VNĐ) |
|---|---|
| Light Trucks | 1,500,000 – 3,000,000 |
| Medium Trucks | 2,500,000 – 5,000,000 |
| Heavy Trucks | 4,000,000 – 8,000,000 |
Note: Prices are for reference only. Actual prices may vary depending on the vehicle model, manufacturer, dealer, and time of purchase.
Radiator Use and Maintenance Tips
- Regularly check the coolant level in the overflow tank, ensuring it’s between the minimum and maximum lines.
- Use specialized coolant; avoid using plain water as it can cause rust and clog the system.
- Clean the radiator periodically, removing dust, debris, and insects to ensure optimal heat dissipation.
- Inspect and replace the radiator cap when necessary, ensuring the pressure valve functions correctly.
- If you encounter any cooling system issues, take your vehicle to a reputable garage for inspection and timely repairs.
The image below illustrates the car radiator cleaning process:
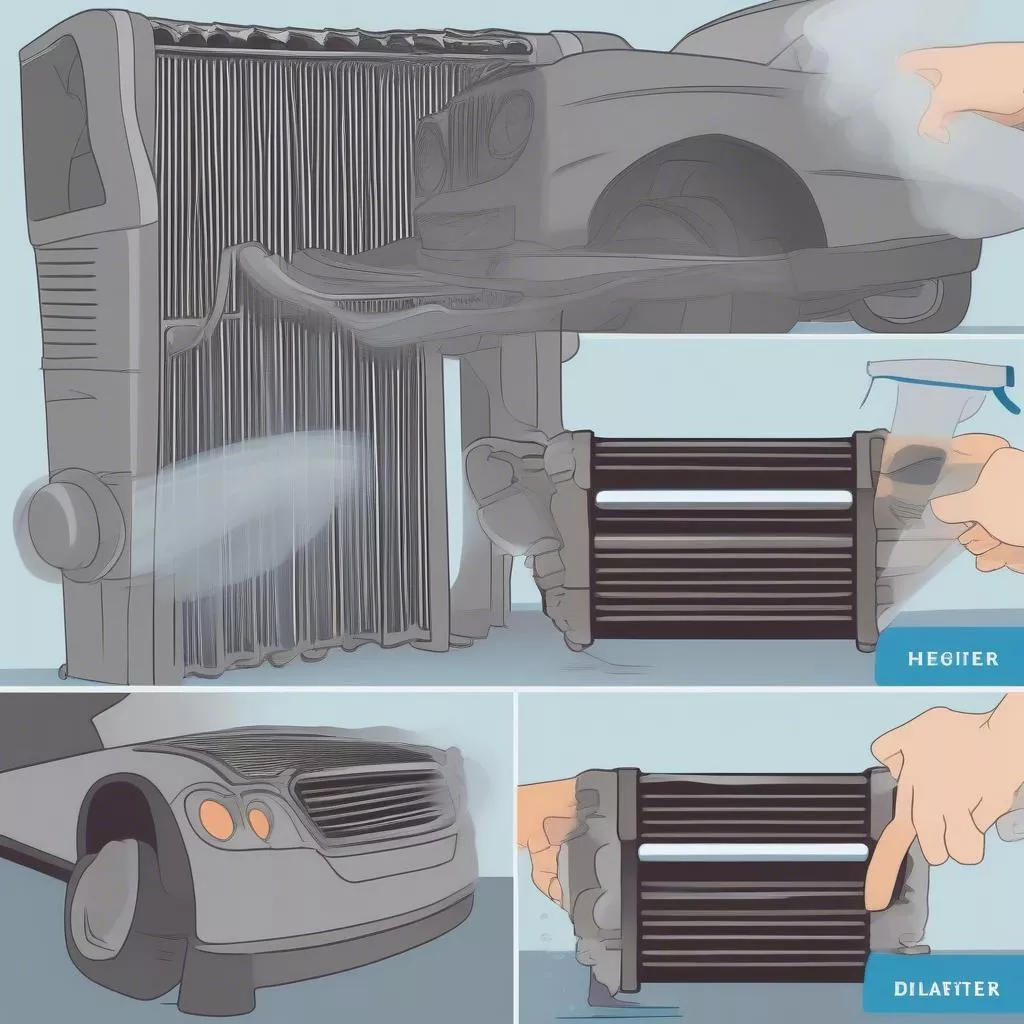 Cleaning a car radiator
Cleaning a car radiator
Frequently Asked Questions About Car Radiators
1. When should a car radiator be replaced?
Replace the radiator if there are signs of leakage, severe blockage, or if it’s been used for an extended period (typically 3-5 years).
2. How to choose the right car radiator?
Choose a genuine radiator that suits your vehicle model and usage needs. Consult with experts or technicians for the most suitable product.
For a clearer understanding of the car radiator replacement process, refer to the image below:
About us

Chúng Tôi luôn muốn trao đến tay khách hàng một sản phẩm tâm đắc nhất, một chiếc XE TẢI tốt nhất mà mọi người luôn muốn sở hữu.








