How Government Policies Influence Exchange Rates
Government policies significantly impact exchange rates, a crucial aspect of macroeconomics. Exchange rates constantly fluctuate due to various factors, with government policies playing a pivotal role. This article delves into how these policies affect exchange rates and their consequences.
Monetary Policy and Exchange Rates
Monetary policy, encompassing tools like interest rates, reserve requirements, and open market operations, directly influences exchange rates. When the central bank raises interest rates, foreign investment flows into the domestic market, increasing demand for the local currency and causing its value to appreciate. Conversely, lowering interest rates reduces the currency’s attractiveness, leading to depreciation. Changes in reserve requirements and open market operations also affect the supply and demand of foreign currency, thereby impacting exchange rates.
Fiscal Policy and Exchange Rates
Fiscal policy, including decisions on government spending and taxation, also affects exchange rates. Expansionary fiscal policy, characterized by increased government spending and tax cuts, can stimulate economic growth, attract foreign investment, and strengthen the local currency. However, if it leads to high inflation, it can erode confidence in the currency, causing depreciation. Conversely, contractionary fiscal policy can weaken the exchange rate.
Trade Policy and Exchange Rates
Trade policy, encompassing measures like tariffs, quotas, and other trade barriers, can also influence exchange rates. Imposing import tariffs may reduce demand for foreign currency, leading to appreciation of the domestic currency. However, if these measures trigger trade wars and reduce exports, they can put downward pressure on the currency.
Similar to China’s exchange rate policy, Vietnam also uses market intervention measures to stabilize its exchange rate.
Foreign Exchange Market Intervention
The central bank can directly intervene in the foreign exchange market by buying or selling foreign currency to influence the exchange rate. When the central bank buys foreign currency, the supply of the domestic currency in the market increases, leading to depreciation. Conversely, when it sells foreign currency, the domestic currency supply decreases, causing appreciation. This mirrors Japan’s exchange rate policy in maintaining currency stability.
Other Macroeconomic Policies
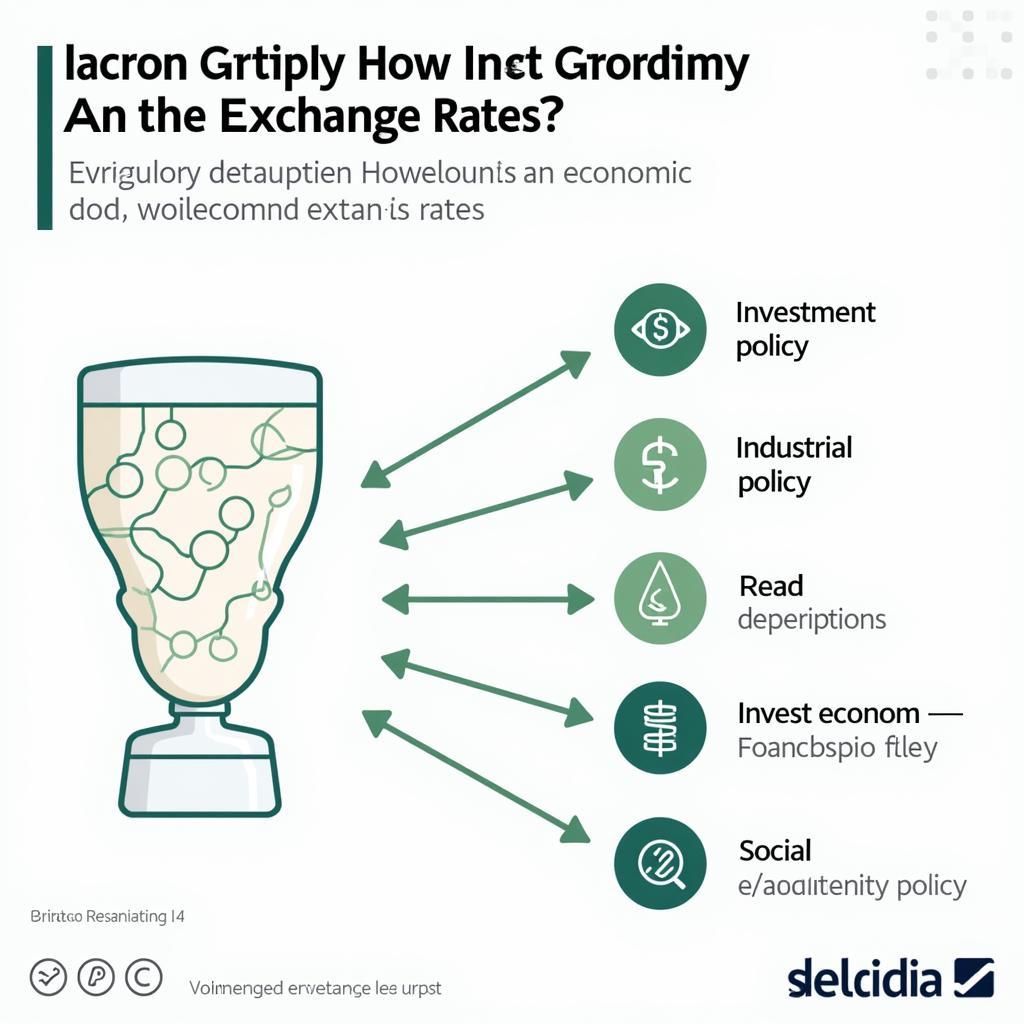
Other macroeconomic policies, such as investment policies, industrial policies, and social policies, can indirectly influence exchange rates through their impact on economic growth, inflation, and investment flows. Economics and policy are closely intertwined.
 Macroeconomic policies impacting exchange rates
Macroeconomic policies impacting exchange rates
Conclusion
Government policies influence exchange rates in various ways. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for policymakers, businesses, and investors to make informed decisions. A stable and appropriate exchange rate plays a vital role in maintaining macroeconomic stability and promoting sustainable economic growth.
FAQ
- How does monetary policy affect exchange rates?
- What role does fiscal policy play in adjusting exchange rates?
- What are the measures for foreign exchange market intervention?
- How does trade policy impact exchange rates?
- How can exchange rate fluctuations be predicted based on policy?
- How do exchange rates affect imports and exports?
- Which policy has the strongest impact on exchange rates?
Contact us for support: Phone: 0968239999, Email: [email protected] or visit us at: TT36 – CN9 Road, Tu Liem Industrial Zone, Phuong Canh Ward, Nam Tu Liem District, Hanoi. We have a 24/7 customer support team. For more information on topics like Vincom’s dividend policy or ESOP policy, visit our website.
About us

Chúng Tôi luôn muốn trao đến tay khách hàng một sản phẩm tâm đắc nhất, một chiếc XE TẢI tốt nhất mà mọi người luôn muốn sở hữu.








