Understanding the Truck Alternator: Powering Your Heavy Duty Vehicle
Have you ever wondered how your truck engine roars to life and powers tons of cargo across challenging terrains? The secret lies in the heart of the engine – the alternator. This vital component acts as a mini power plant, supplying electricity to your truck’s entire electrical system. It converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical power, fueling everything from headlights and the radio to the AC system and countless other essential components.
The Importance of the Truck Alternator
The alternator is crucial for your truck’s operation. A malfunctioning alternator can leave you stranded, as the electrical system will be without power.
Technical Perspective
Alternators operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction. As the engine runs, the alternator’s rotor spins, generating a rotating magnetic field. This field interacts with stationary coils (stator), producing an alternating current (AC). A rectifier then converts the AC to direct current (DC), suitable for powering the truck’s electrical systems.
Economic Perspective
Alternators can be costly to replace, but their role in maintaining your truck’s operation is invaluable. A breakdown can lead to expensive repairs, replacements, and lost productivity due to downtime.
Cultural Significance
In some Eastern cultures, the alternator symbolizes dynamism and power. It’s often seen as the “heart” of the vehicle, the source of its strength and vitality.
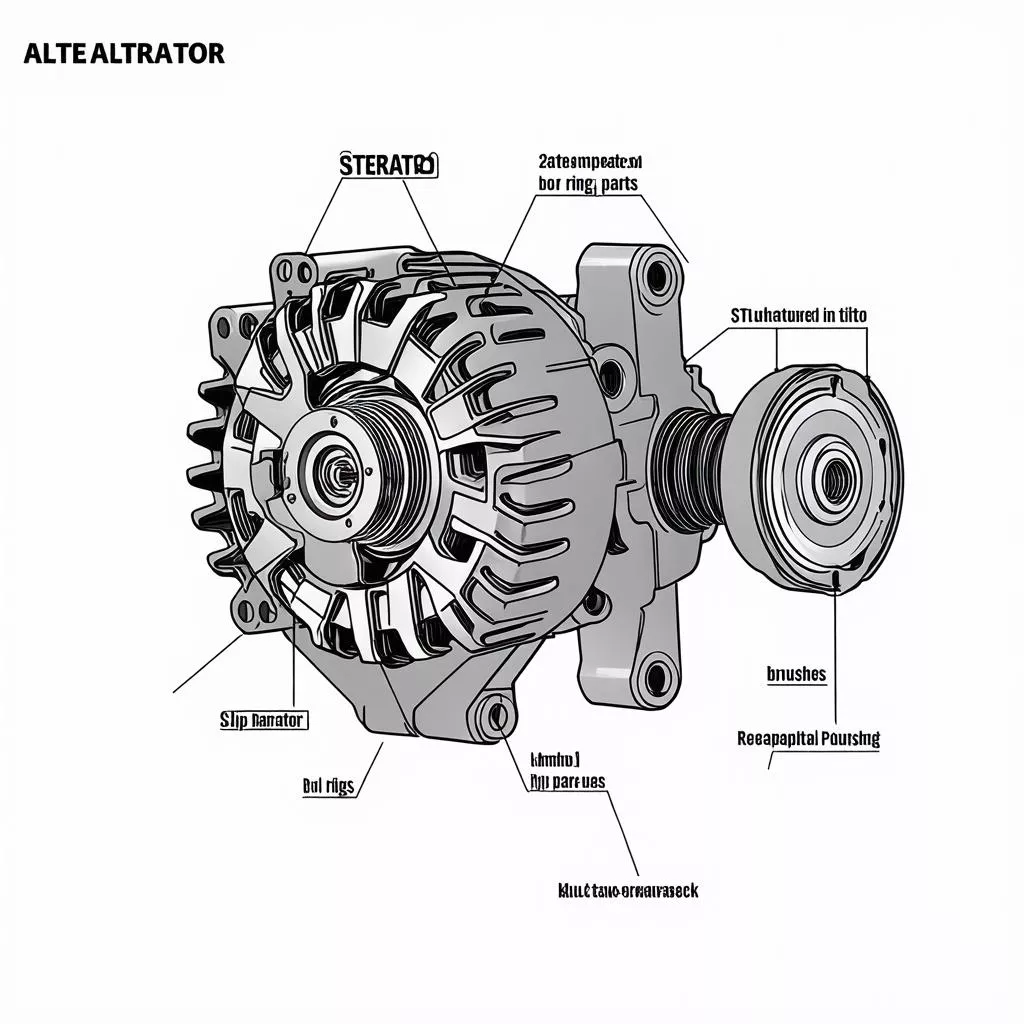
Components of a Truck Alternator
The alternator comprises several key components, each with a specific function.
 Diagram of a truck alternator
Diagram of a truck alternator
1. Rotor: The rotating part of the alternator, connected to the engine’s crankshaft. The rotor houses electromagnets wrapped in wire. As the engine turns, the rotor spins, creating a rotating magnetic field.
2. Stator: The stationary part of the alternator, containing fixed coils wound around an iron core. The rotating magnetic field from the rotor interacts with these stator coils, generating electricity.
3. Rectifier: Converts the alternating current (AC) produced by the stator into direct current (DC) to power the truck’s electrical system.
4. Voltage Regulator: Controls the alternator’s output voltage, ensuring a stable supply of power to the electrical system.
How it Works
The alternator operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction. As the engine runs, the rotor spins. The electromagnets on the rotor generate a rotating magnetic field. This field cuts across the stator coils, inducing an alternating current (AC). The AC is then converted to direct current (DC) by the rectifier and regulated by the voltage regulator.
Signs of a Failing Alternator
Alternators can fail, and recognizing the warning signs is essential. Common symptoms include:
- Battery Warning Light: A illuminated battery light indicates the battery is discharging and the alternator might not be charging it.
- Dim or Flickering Headlights: The alternator powers the headlights. Dim or flickering lights can signal a problem.
- Malfunctioning Electrical Accessories: Weak or non-functional radio, AC, and other electrical accessories can indicate alternator issues.
- Unusual Noises: Whining, grinding, or squealing sounds from the alternator can indicate bearing or belt problems.
Common Problems
Some common alternator issues include:
- Slow Cranking Speed: The alternator relies on engine speed. Slow cranking can prevent it from generating sufficient power.
- Damaged Wiring: Wiring connecting the alternator to the electrical system can become damaged or corroded.
- Faulty Rectifier: A malfunctioning rectifier prevents AC to DC conversion, hindering power generation.
- Faulty Voltage Regulator: A faulty regulator leads to unstable voltage output, potentially damaging electrical components.
Alternator Maintenance
Regular maintenance can prolong the life of your alternator. Key steps include:
- Inspecting Wiring: Check for damage, corrosion, or loose connections in the alternator wiring.
- Checking Voltage: Use a voltmeter to ensure the alternator is outputting the correct voltage.
- Testing the Rectifier: Verify the rectifier is properly converting AC to DC.
- Replacing Worn Parts: Replace worn belts, bearings, or other components as needed.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I repair an alternator myself?
Repairing an alternator can be complex and potentially dangerous. It’s recommended to consult a qualified mechanic.
Do alternators need periodic replacement?
Alternators typically don’t require scheduled replacement. Replace them only if they malfunction.
Does the alternator affect battery life?
The alternator charges the battery. A malfunctioning alternator can lead to battery overcharging or undercharging, shortening its lifespan.
Next Steps
Contact us for expert advice on truck alternators!
Visit https://xetaihanoi.edu.vn/ban-may-phat-dien-o-to-cu/ to explore our selection of truck alternators.
Browse our website for more truck-related articles: https://xetaihanoi.edu.vn/.
Leave a comment if you have any questions.
Share this article with your friends!
Thank you for reading!
About us

Chúng Tôi luôn muốn trao đến tay khách hàng một sản phẩm tâm đắc nhất, một chiếc XE TẢI tốt nhất mà mọi người luôn muốn sở hữu.








